设置程序
安装最新版本的 TensorFlow
1 | !pip install -q --upgrade tensorflow |
配置导入和 Eager Execution
1 | from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function |
TensorFlow version: 1.9.0-rc2
Eager execution: True导入和解析训练数据集
下载数据集
1 | train_dataset_url = "http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_training.csv" |
Downloading data from http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_training.csv
8192/2194 [================================================================================================================] - 0s 0us/step
Local copy of the dataset file: /content/.keras/datasets/iris_training.csv检查数据: 使用 head -n5 命令查看前 5 个条目:
1 | !head -n5 {train_dataset_fp} |
120,4,setosa,versicolor,virginica
6.4,2.8,5.6,2.2,2
5.0,2.3,3.3,1.0,1
4.9,2.5,4.5,1.7,2
4.9,3.1,1.5,0.1,0解析数据集
1 | def parse_csv(line): |
创建训练 tf.data.Dataset|
1 | train_dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset(train_dataset_fp) |
example features: tf.Tensor([5.8 2.7 4.1 1. ], shape=(4,), dtype=float32)
example label: tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)选择模型类型: 使用 Keras 创建模型
1 | model = tf.keras.Sequential([ |
<tensorflow.python.keras.engine.sequential.Sequential object at 0x7fa0842648d0>训练模型
定义损失和梯度函数
1 | def loss(model, x, y): |
创建优化器
TensorFlow 拥有许多可用于训练的优化算法。此模型使用的是 tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer,它可以实现随机梯度下降法 (SGD)。
1 | optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01) |
训练循环
- 迭代每个周期。通过一次数据集即为一个周期。
- 在一个周期中,遍历训练 Dataset 中的每个样本,并获取样本的特征 (x) 和标签 (y)。
- 根据样本的特征进行预测,并比较预测结果和标签。衡量预测结果的不准确性,并使用所得的值计算模型的损失和梯度。
- 使用 optimizer 更新模型的变量。
- 跟踪一些统计信息以进行可视化。
- 对每个周期重复执行以上步骤。
num_epochs 变量是遍历数据集集合的次数。与直觉恰恰相反的是,训练模型的时间越长,并不能保证模型就越好。
num_epochs 是一个可以调整的超参数。选择正确的次数通常需要一定的经验和实验基础。
1 | ## Note: Rerunning this cell uses the same model variables |
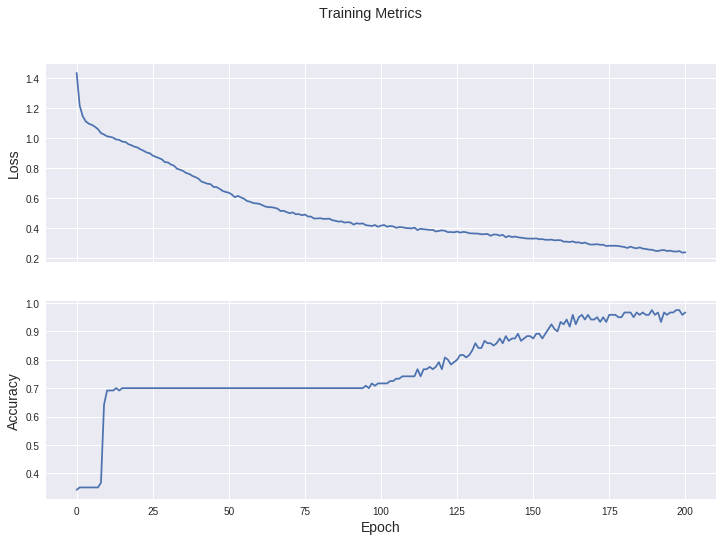
Epoch 000: Loss: 1.433, Accuracy: 34.167%
Epoch 050: Loss: 0.636, Accuracy: 70.000%
Epoch 100: Loss: 0.417, Accuracy: 71.667%
Epoch 150: Loss: 0.331, Accuracy: 87.500%
Epoch 200: Loss: 0.239, Accuracy: 96.667%可视化损失函数随时间推移而变化的情况
1 | fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, sharex=True, figsize=(12, 8)) |
评估模型的效果
设置测试数据集
1 | test_url = "http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_test.csv" |
Downloading data from http://download.tensorflow.org/data/iris_test.csv
8192/573 [============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================] - 0s 0us/step根据测试数据集评估模型
1 | test_accuracy = tfe.metrics.Accuracy() |
Test set accuracy: 96.667%使用经过训练的模型进行预测
1 | class_ids = ["Iris setosa", "Iris versicolor", "Iris virginica"] |
Example 0 prediction: Iris setosa
Example 1 prediction: Iris versicolor
Example 2 prediction: Iris virginicacolab地址
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1iGHulgf_ioKl_GP_7_v8yTwwyfzP6KTR

